Stats
Extra Credit: 40 pts
(At 100 points of EC you will get a free slice of pizza)
Lesson Materials/Recap
Boolean logic review
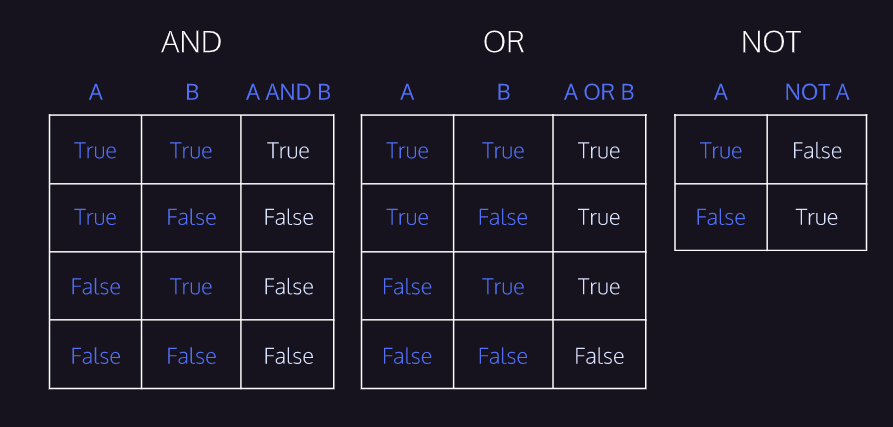 Make sure you understand these.
You can also string these expressions together.
eg: ` (a > 0) and (b > 0) `
this works because `>` is a boolean operator so `a > 0` returns a boolean value, and `and` needs boolean values on both sides to work
If you string to many together it can get confusing, so make sure to use parentheses
But remember at the end of the day, it all evaluates to one boolean value (True or False), and the place you put the expression, such as an if statement, just sees that value, because the expression will be evaluated before the if statement sees it.
Make sure you understand these.
You can also string these expressions together.
eg: ` (a > 0) and (b > 0) `
this works because `>` is a boolean operator so `a > 0` returns a boolean value, and `and` needs boolean values on both sides to work
If you string to many together it can get confusing, so make sure to use parentheses
But remember at the end of the day, it all evaluates to one boolean value (True or False), and the place you put the expression, such as an if statement, just sees that value, because the expression will be evaluated before the if statement sees it.
For loops lesson
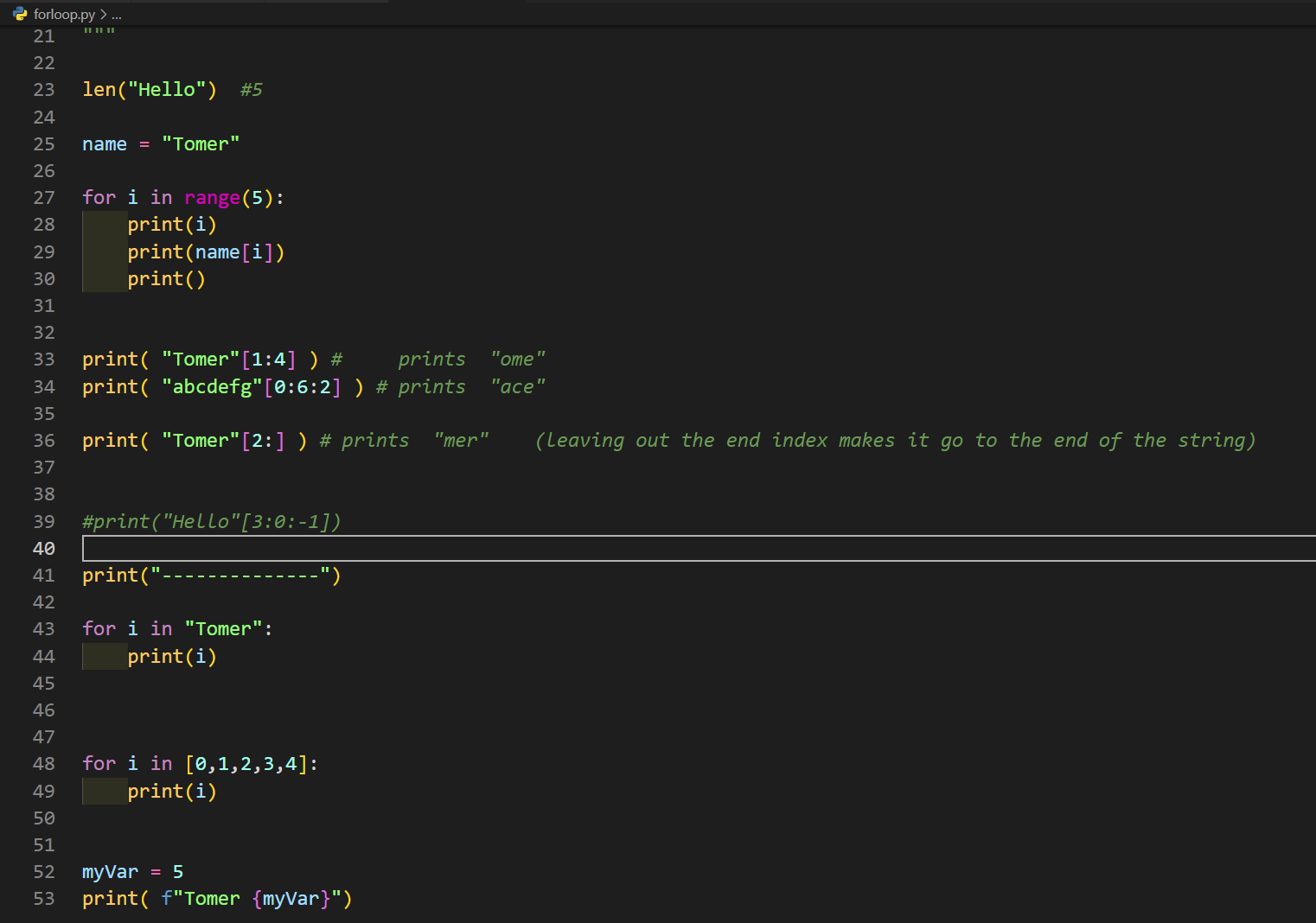
Homework
Lesson 2 Homework
1. Please do the quiz linked at the bottom of this page.
2. Please do this problem on HackerRank. (You will need to make an account sorry).
Write all your code inside of the provided if statement block (under
if __name__ == main:)
Optional extra homework: feel free to do the next hackerrank challenge after you are done with the one linked above. (It should be the one called "Arithmetic Operations")
Lesson 3 Homework (More if practice)
1. Please solve the following Problem completely on your own:

2. Extra Credit:
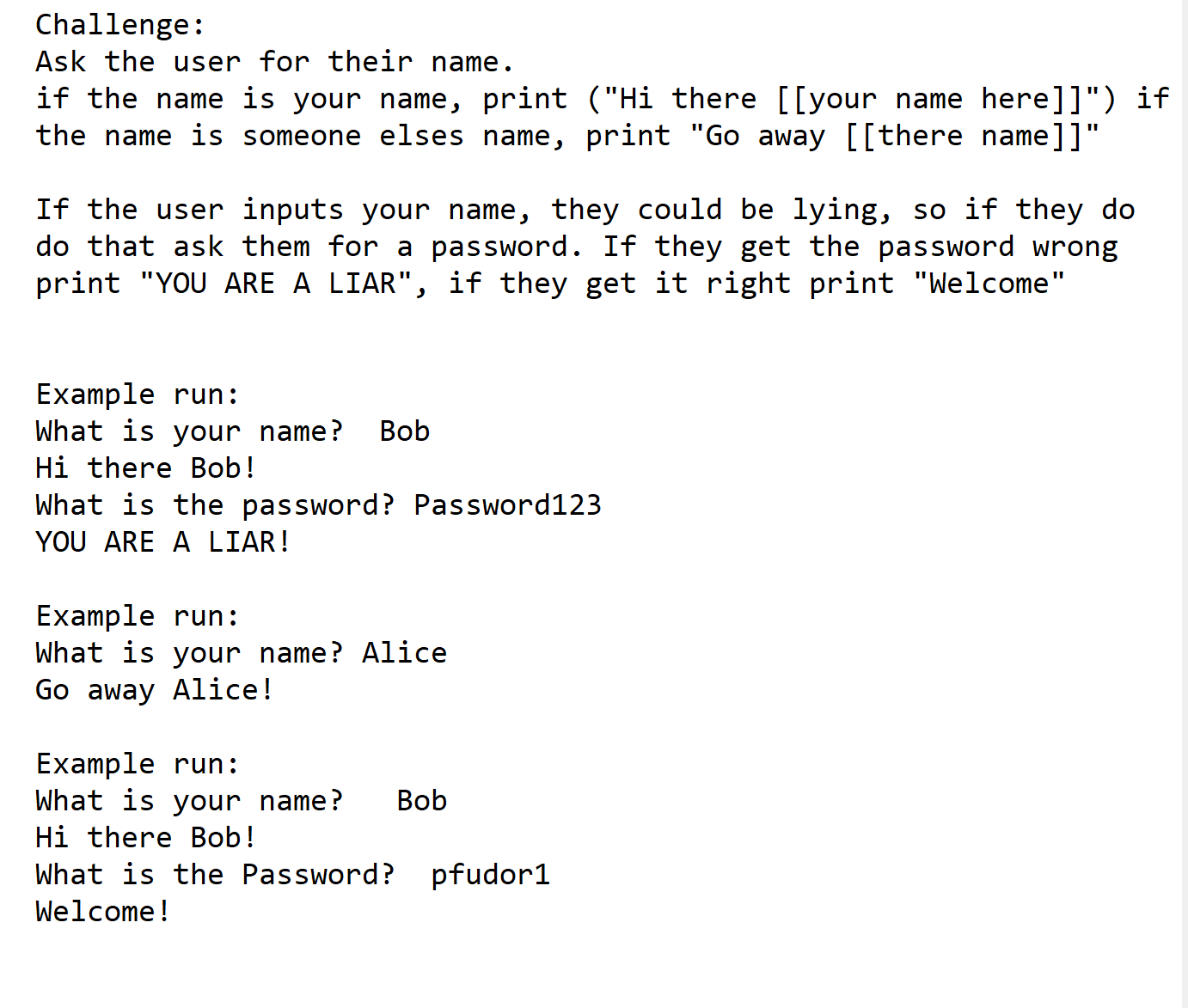
Lesson 4 Homework (Functions, arguments and return)
Please do all of the following:
1. Please solve this HackerRank problem relating to writing a function and if statements
2. Please solve this codingbat challenge (hint: built in `len()` function returns length of a string),
3. Please solve this: this codingbat challenge
4. do the following exercise from the slides:

5. Extra Credit No longer Extra Credit:

Hint
you can call functions recursively, meaning you can call the function you are currently in from within itself6. Extra Credit: do this coding bat challenge in 1 line of code. Read the section below this to help you out.
Hint: they already got it down to 3 lines right?, how could you use the same strategy as them to do it in 1 line (return a boolean directly that is derrived from a boolean expression made using ands/ors )
Lesson 6-ish Homework (While loops)
Please do all of the following:
1. Please solve this HackerRank problem.
Two facts that may or may not come in handy:
1) ``` my_string_var += "something" ``` is shorthand for ```my_string_var = my_string_var + "something" ``` and can help you build up a string
2) ``` print("some text", end="") ``` will print to the console without making a new line
2. Write a function that takes in a number as a parameter and returns the factorial of the number. The function should have a while loop inside it and is not allowed to call itself
Tips: 1) look at slides for example of how they use while loop. 2) if you need to debug your code put print statements in the while loop that print out each of the variables (eg `print(x,y,z)`), so you can follow in your head what code is run when and how all the values are changing
3. Extra Credit: Get 100% on this quiz about while loops. (it's written in javascript though)
Lesson 7 & 8 Homework (for loops + string indexing) -- IGNORE FOR NOW
1. Make yet another function to calculate the factorial, this time using for loops instead of while loops. Also try to use good variable names if you can.
2. Do this hackerrank problem.
This one is a bit hard, but you can do it using what we've learned so far (see class recap screenshot at top of page): namely using for loop and string slicing (the thing with string_var[start:end:step]). of course you can use variables inside the brackets
Tips:
- print statements. Print what is going on at each stage of the loop, print what variables are and see if they are what you'd expect.
- However once you're ready to submit comment out the print statements so hackerrank accepts it
- use pointless variables (with good names): ie if a line of code gets to complicated then you can extract parts of it into named variables. This way you can edit each part of it separately and also test each part is what you would expect by printing it.
try your best if you don't succeed we'll go over it in class
3. Extra Credit: Do 3 or more codingbat problems from any section other than warmup
4. Fizzbuzz is a classic coding challenge problem that is pretty simple and is used to verify if someone even knows the basics of how to code, and to see how they think about optimizing their code. The homework assignment is just to complete it correctly.
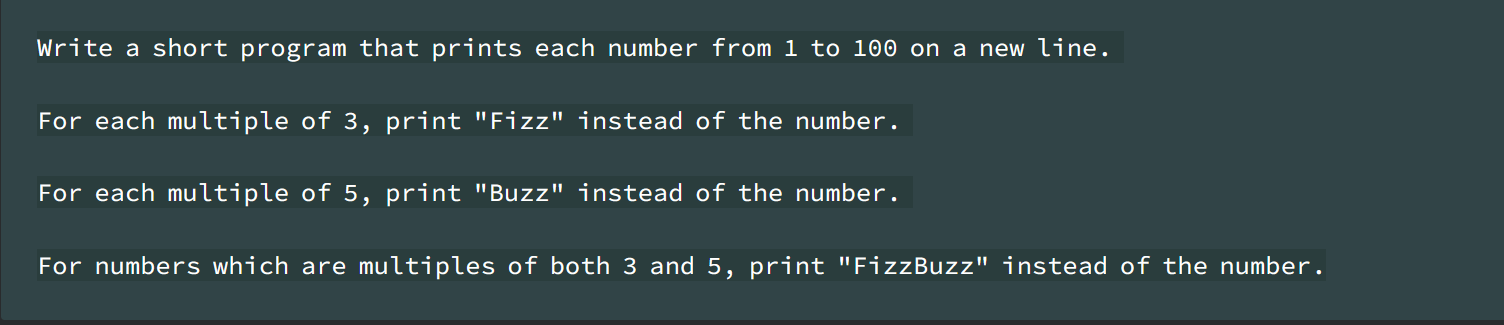
Lesson 10 Homework
-
mean median (you can use list.sort() to sort the list if you want)
mode(lets save mode till we learn about list more) for loop challenge - Write a program that repeatedly prompts a user for integer numbers until the user enters 'done'. Once 'done' is entered, print out the largest and smallest of the numbers. If the user enters anything other than a valid number catch it with a try/except and put out an appropriate message and ignore the number.